The initial wave of switches featuring 800G ports has entered the market, facilitating a comprehensive evaluation of opportunities and strategic deployment planning by service providers. Accompanying this release are 800G client-side optical modules, designed to support either two 400GE connections or eight 100GE connections. Furthermore, as industry standards continue to evolve, an 800GE version is poised for introduction. The advancement from 400G to 800G technology streamlines this transition, simplifying the adoption of dual-density optical modules and branching connection methodologies.
The emergence of 800G switch ports, optical modules, and Direct Attach Cables (DACs) presents an enticing prospect for service providers aiming to enhance network performance without delay, bypassing the need to await the formalization of the 800GE standard. In parallel, the ongoing efforts of the IEEE 802.3df 800G and 1.6T working groups, coupled with notable industry progressions, ensure the formulation of a robust roadmap for forthcoming upgrades. The swift deployment of 400G technology signifies the industry’s agility in delivering cutting-edge solutions, thus aligning with the imminent shift towards 800G as service providers expand and modernize their data center infrastructure.
The release of 25.6T switches with 800G ports creates new opportunities for data center operators, leveraging networks that significantly enhance performance while reducing complexity, costs, and power consumption.
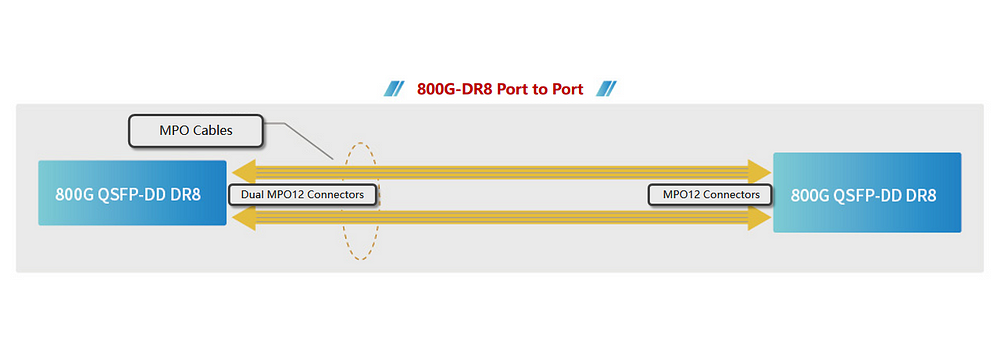
As depicted in Figure 1, a single 25.6T switch can replace six 12.8T switches. Each 800G port on the 25.6T switch comprises 8x 100G PAM4 channels and will support 8x 100GE connections, two 400GE connections, or a single 800GE interface. By utilizing 100G PAM4 serial interfaces, the number of signal channels on the 25.6T switch matches each one of the six 12.8T switches, reducing the overall complexity of the solution. Replacing six switches with one at the same 25.6T network capacity significantly decreases power consumption and costs.
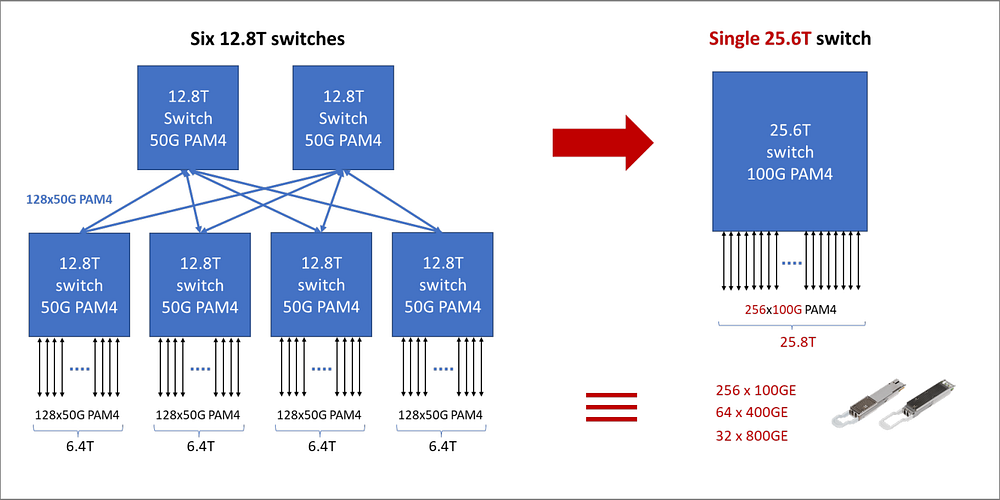
Figure 2 depicts a 25.6T platform equipped with 800G ports, featuring 32 ports in a compact 1RU form factor, supporting 64 400GE links or 256 100GE links using breakout cables. Several use cases exploring this flexibility are discussed below.

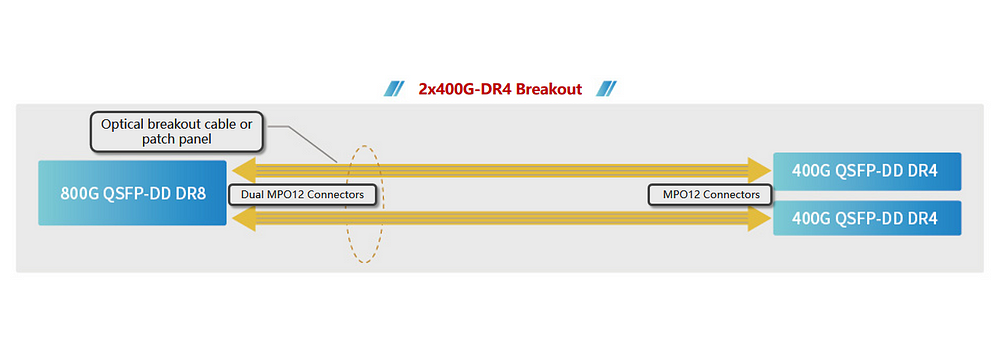
Figure 3 illustrates an 800G port supporting two IEEE 400G BASE-FR4 connections extending up to 2km, offering high-density 400G interfaces. Compared to 12.8T systems, the configuration using breakout cables enables a doubling of the 400GE link count supported by the 1RU 25.6T switch system. Deployments with this versatile configuration are progressing in various applications, including high-density AI/ML clusters and ultra-high-definition video processing in data centers.
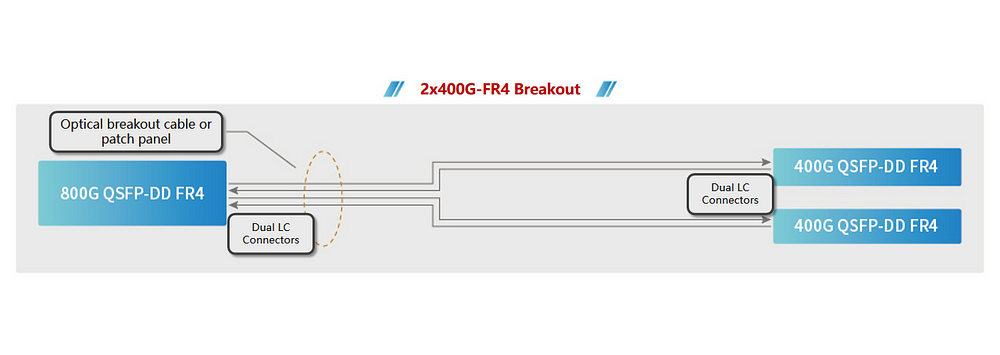
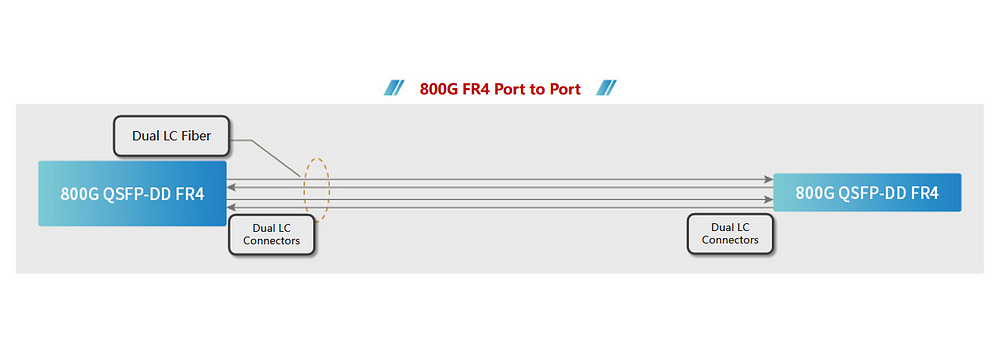
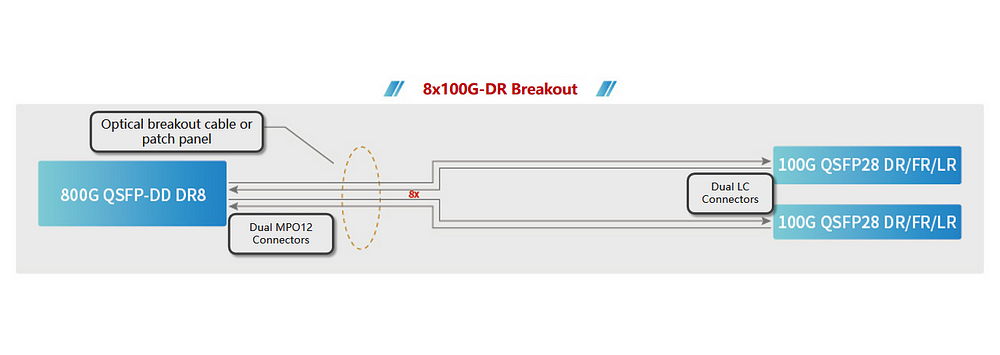
Figure 4 illustrates an 800G port supporting 8 IEEE 100GBASE-DR (up to 500m)/IEEE 100GBASE-FR (up to 2km)/IEEE 100GBASE-LR (up to 10km) connections, offering high-density 100G interfaces. The figure displays branching into 8 independent 100G links, branching into two 400G connections, and an 800G direct connection. These configurations are highly suitable for upgrades in peer/hosted networks and distributed data centers requiring numerous 100GE network connections.
800G technology undoubtedly stands as a significant driving force in the field of communications, leading us towards an unprecedented future of high-speed, high-efficiency, and highly interconnected networks in the upcoming digital era. Its outstanding transmission speed and vast bandwidth enable various industries to embrace new application scenarios and innovative opportunities.

Reference: “800G Client Optics in the Data Center — A Heavy Reading white paper produced for Cisco,” SIMON STANLEY, ANALYST AT LARGE, HEAVY READING
