Decoding the Potential – 400G Optical Modules for Next-Gen DCI

From the data center network architecture perspective, transitioning from existing 100G solutions to meet the same-scale data center’s non-blocking network throughput has posed several challenges. Achieving this objective requires adding more ports, expanding rack space to accommodate servers and switches, and providing more server rack space. This approach is not only uneconomical but also significantly increases the complexity of the network architecture.
In contrast, transitioning from 100G to 400G is a more cost-effective way to provide higher bandwidth for data centers while reducing network architecture complexity. Furthermore, following the natural progression of network equipment development, when the interface speed increases fourfold to reach 400G, given mature device and transceiver technologies, the cost of a 400G network device typically amounts to only about 50% of the cost of four 100G devices and interfaces.
400G Optical Modules in Data Center
400G has already become ubiquitous in data center applications.
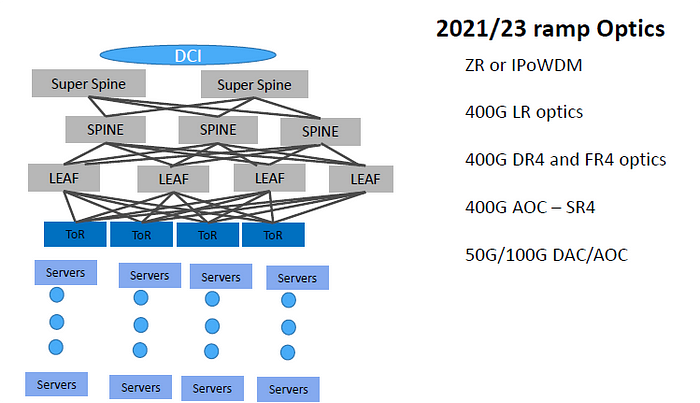
400G already become a must-have optical communication solution in DCI scenarios.
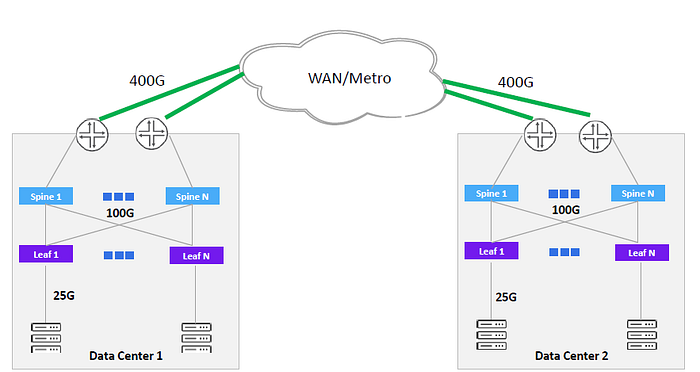
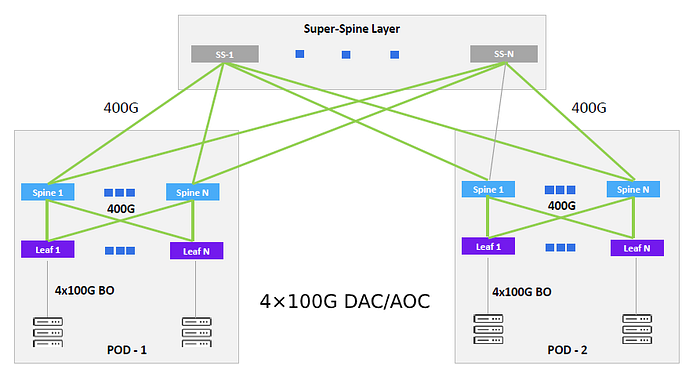
400G becomes the first choice for Hyperscale in POD interconnects.
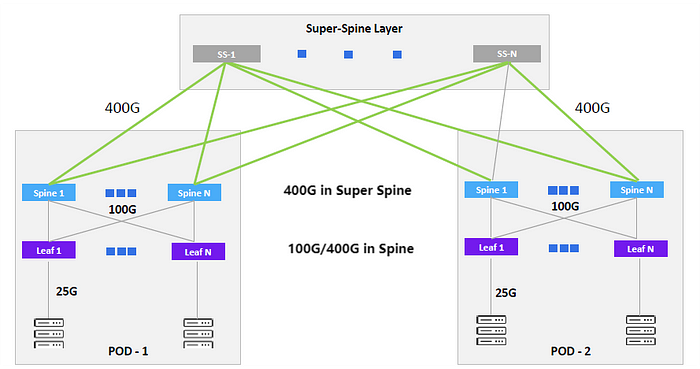
Note: POD (Point of Delivery) is a distribution point that is used to facilitate resource pooling in a data center. To achieve this, a physical data center is typically divided into one or more physical zones, with each zone referred to as a POD. Thus, POD is a physical concept and represents the fundamental deployment unit of a data center. Typically, one piece of physical equipment can only belong to one POD.
ToR-Server, 100G Downlink 400G Uplink
Market Forecast and Iteration Direction of 400G in Data Center Technology
Market Forecast for 400G and Higher Speed Optical Modules
According to Light Counting’s projections for 400G and 800G-related products, SR/FR series optical modules are expected to be the primary growth products in data centers and internet centers:
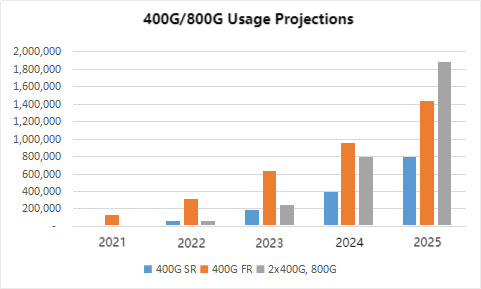
The forecast indicates that 400G rate optical modules will be deployed on a large scale in 2023 and will account for the majority of optical module (40G and above rate) sales in 2025:
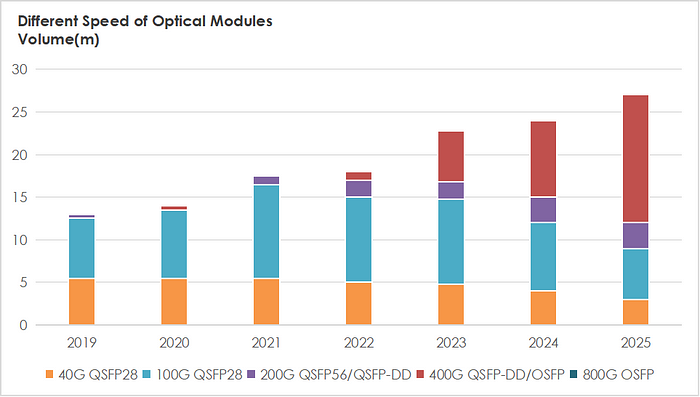
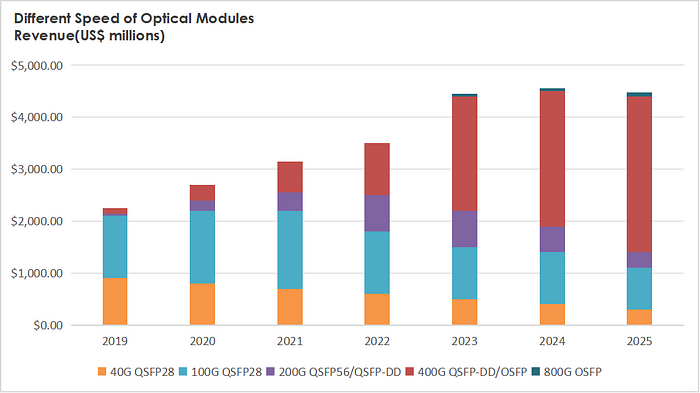
400G Optical Module Iteration Trends
With the physical layer single-lane electrical port speed reaching 112Gbps, data center networks will face significant challenges in network system design, equipment design, key component design, and more.
In this context, on June 13, 2021, the QSFP112 MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) group officially released the new QSFP112 specification 1.0. A total of 31 companies came together to support the QSFP112 MSA, with founding members including companies like Accelink Technologies, Alibaba, Amphenol, Baidu, Credo, H3C, Hisense, and others, to meet the industry’s demand for high-speed, high-density network solutions. The MSA will significantly help traditional QSFP users upgrade their link bandwidth to 400G per port with lower costs and shorter transition times.
From the different perspectives of 112G high-speed system design, the study of high-speed system design, system test methodology, high-speed interconnect system simulation, printed circuit board design for next-generation devices, high-speed backplane connectors, I/O connectors, and high-speed copper cables design and application for network devices under 112G SerDes are described in several aspects. All these efforts are aimed at accelerating the technological innovation of 112G SerDes-based networking devices.
In China, major domestic internet companies like Alibaba, Baidu, JD.com, ByteDance, and Kuaishou, while still primarily using 25G or 56G electrical ports in their current data center architectures, are jointly planning for high-speed electrical interfaces based on the 112G SerDes for their next-generation data centers.
In the optical module industry, GIGALIGHT has introduced 400G QSFP112 AOC/VR4/SR4 modules. Similarly, other companies such as Accelink, InnoLight, and Eoptolink have introduced their own 400G QSFP112 products and initiated validation plans with internet companies.
400G QSFP112 SR4/FR4/DR4 modules operating at 112Gbps SerDes speeds will undoubtedly be massively deployed during the process of upgrading from 100G to 400G in next-generation data centers.
